Understanding Steel Fabrication: The Basics
When exploring the realm of industrial processes, one cannot overlook the significance of a steel fabrication shop. These hubs of creativity and engineering are essential to the construction and manufacturing industries, serving as the backbone for various structures and components. Understanding the fundamental aspects of steel fabrication is crucial for professionals, businesses, and anyone interested in the mechanics of modern construction.
What is a Steel Fabrication Shop?
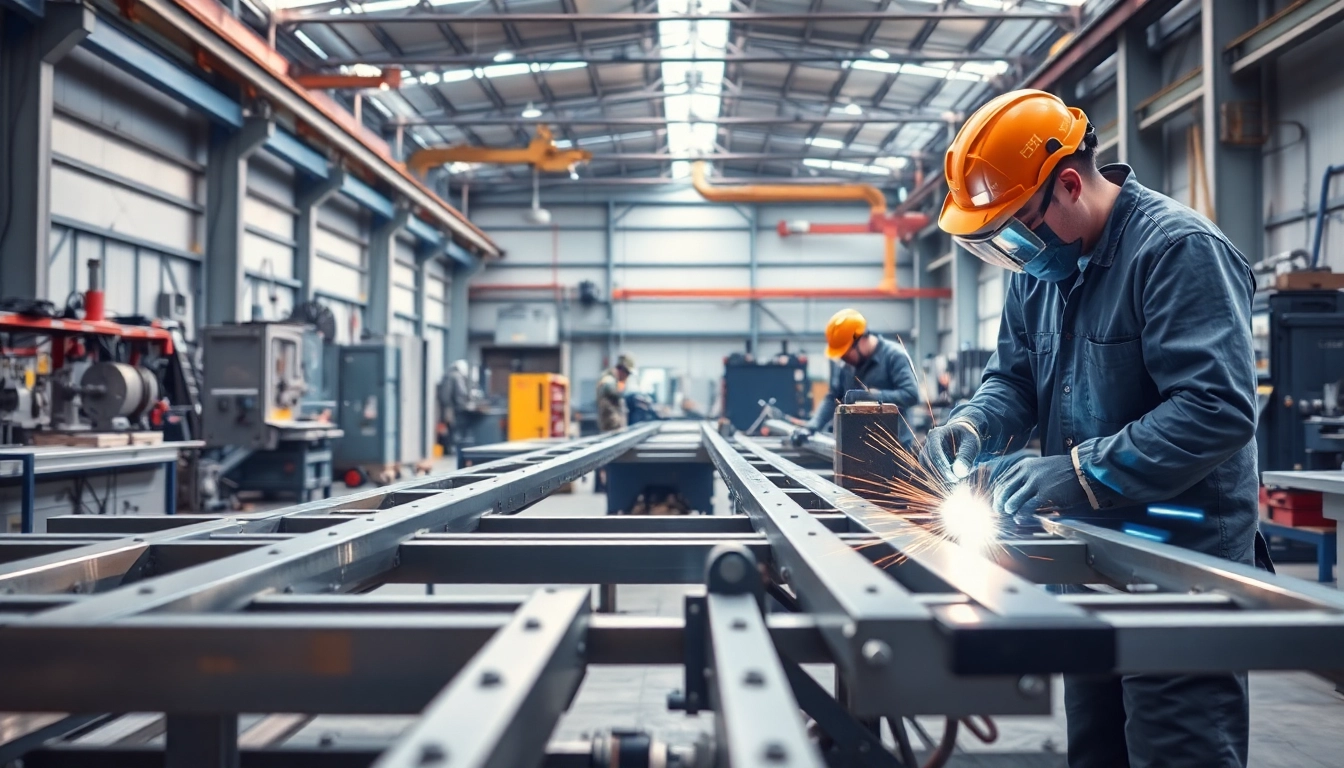
A steel fabrication shop is a specialized facility where raw steel materials are transformed into finished products or components ready for installation or assembly. These shops are equipped with various tools and machinery, operated by skilled technicians and engineers who bring designs to life. Fabrication can range from simple components, such as brackets and beams, to complex structures like bridges and skyscrapers. The process often involves cutting, shaping, and assembling raw materials following specific project specifications.
Key Processes in Steel Fabrication
The fabrication process typically encompasses several key stages, each integral to ensuring the quality and precision of the final product:
- Cutting: The initial step involves cutting steel materials into specific shapes and sizes using saws, lasers, or water jets.
- Drilling: Holes are drilled into the steel for fasteners and fittings, which is crucial for assembly.
- Forming: This process shapes steel through bending, rolling, or forging to meet design specifications.
- Welding: The most critical aspect of fabrication, welding involves joining pieces together to create a single, sturdy unit. Different techniques, such as MIG, TIG, and Arc welding, may be employed based on material and design.
- Finishing: The final step may include applying coatings for corrosion resistance, polishing for aesthetic appeal, or heat treatment for added strength.
Common Tools and Equipment Used
To achieve precise fabrication results, a steel fabrication shop utilizes a variety of tools and equipment. Among the most common are:
- Cutting Tools: Band saws, plasma cutters, and laser cutters for accurate shape production.
- Drilling Machines: Various drill presses and CNC machines designed for different drilling operations.
- Forming Equipment: Press brakes, rollers, and hammers to manipulate and form metal.
- Welding Machines: Arc, MIG, and TIG welders essential for joining materials securely.
- Inspection Tools: Equipment like calipers and micrometers to measure and ensure precision in components.
Essential Skills for Steel Fabrication Professionals
Those working in a steel fabrication shop are required to possess a unique set of skills to navigate the complexities of the industry successfully. Mastery of these skills not only ensures high-quality output but also contributes to safe working conditions.
Technical Skills Required for the Job
Technical skills form the foundation of a successful career in steel fabrication. Professionals must have a solid understanding of:
- Blueprint reading: The ability to interpret technical drawings and specifications accurately.
- Material properties: Knowledge of different steel grades and their characteristics to determine appropriate usage.
- Welding and fabrication techniques: Proficiency in various welding methods, including knowledge of the correct parameters and settings.
- Mechanical aptitude: Familiarity with tools and machinery, as well as troubleshooting skills for maintenance and repairs.
Importance of Safety Training
Safety cannot be overstated in steel fabrication environments. The industry involves handling heavy materials, operating powerful machinery, and working in potentially hazardous settings. Effective safety training programs must include:
- General workplace safety practices, including awareness of surroundings and proper lifting techniques.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE) usage: Training on appropriate gear, such as helmets, gloves, and eye protection.
- Emergency procedures: Clear protocols that outline what to do in case of accidents or equipment failure.
- Regular workshops and updates to reinforce safety standards and practices continually.
Certifications and Qualifications
While formal education is beneficial, many skills in steel fabrication are acquired through hands-on experience and apprenticeships. However, obtaining relevant certifications can significantly enhance a professional’s credentials. Common certifications in the field include:
- Welder Certifications: Certifications from the American Welding Society (AWS) or similar organizations.
- CNC Machining Certifications: Recognition for proficiency in operating CNC machines.
- OSHA Training: Completion of OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) training programs for workplace safety compliance.
High-Quality Standards in Steel Fabrication
High-quality standards are vital in steel fabrication, as they directly impact the safety, reliability, and longevity of the end products. Various methods and practices ensure these standards are upheld throughout the fabrication process.
Quality Control Measures
Implementing stringent quality control measures in a steel fabrication shop is necessary to monitor and ensure adherence to specifications. These measures often include:
- Regular inspections: Conducting visual and dimensional inspections of components at multiple stages of production.
- Testing: Employing destructive and non-destructive testing methods to assess weld integrity and material strength.
- Documentation: Maintaining records of inspections, tests, and compliance with regulations to track quality history.
Industry Standards and Regulations
Steel fabrication is subject to various industry standards and regulations that dictate safety and quality. It is essential for shops to comply with these standards, which may include:
- ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) standards, which provide specifications for steel materials.
- ISO (International Organization for Standardization) certifications related to quality management systems.
- Local building codes and regulations, ensuring structures are safe and compliant with municipal standards.
Best Practices for Maintaining Quality
To maintain high-quality standards, fabrication shops may adopt a series of best practices, including:
- Investing in skilled personnel who continually refine their expertise through training.
- Using high-quality materials and validated suppliers to ensure raw material integrity.
- Utilizing advanced technological solutions, such as CAD/CAM software for precision and efficiency.
- Conducting routine maintenance on equipment to prevent malfunctions and ensure operational consistency.
Challenges Faced in a Steel Fabrication Shop
Every steel fabrication shop encounters challenges that can affect productivity, quality, and safety. Identifying and addressing these challenges is critical for business success.
Common Operational Challenges
Operational efficiency can be hindered by various challenges, including:
- Labor shortages: Difficulty in finding skilled workers can compromise production timelines and quality.
- Downtime: Unplanned machinery breakdowns can disrupt workflows and delay project completion.
- Supply chain issues: Variability in supply chain performance can impact material availability and lead times.
Handling Material Defects
Material defects can arise at any stage of the fabrication process, often affecting the integrity of the finished product. Effective strategies for handling defects include:
- Implementing quality checks at each phase of production to catch issues early.
- Training staff to identify and address defects immediately, minimizing waste.
- Worked closely with suppliers to ensure material quality and reduce the occurrence of defects.
Adapting to Market Changes
The steel fabrication market is subject to fluctuations due to changes in demand, technology, and regulations. Successful shops need to adapt by:
- Staying informed of market trends and forecasts to align production strategies.
- Embracing innovation, such as automation in production processes, to enhance competitiveness.
- Developing flexible workflows that allow for adjustments based on current demands.
The Future of Steel Fabrication Shops
As technology and environmental concerns evolve, so does the landscape of steel fabrication. The future points to innovative practices and shifts that will redefine the industry.
Emerging Technologies in Steel Fabrication
Advancements in technology are revolutionizing how steel fabrication shops operate, with innovations like:
- 3D Printing: Increasingly, shops are utilizing 3D printing for complex designs and rapid prototyping.
- Automation and Robotics: Automated machinery can reduce manual labor and increase production efficiency with precision.
- Digital Fabrication: Integration of digital technologies for design and manufacturing aids in achieving precision and consistency.
Sustainability Practices in the Industry
Sustainability is a growing focus in manufacturing, including steel fabrication. Shops are incorporating practices such as:
- Recycling scrap metal to minimize waste and reduce overall material costs.
- Utilizing eco-friendly materials or processes to lessen the environmental impact.
- Implementing energy-efficient machinery and practices to lower energy consumption.
Career Opportunities and Growth
The outlook for careers within steel fabrication remains promising, with numerous opportunities for advancement. Potential paths include:
- Leadership roles: Progressing to supervisory or managerial positions overseeing projects and teams.
- Specialization: Focusing on niche areas like welding certification, CNC machining, or quality control.
- Consultative roles: Providing expertise to improve processes for other fabrication shops or related industries.
In conclusion, the world of steel fabrication is complex, vibrant, and integral to construction. Understanding its fundamental processes, skills, challenges, and future trends is paramount for anyone interested in this dynamic industry.