Understanding Inflammation and Its Impact on Health
What is Inflammation?
Inflammation is a natural and vital part of the body’s immune response to injury or infection. It acts as a defense mechanism, helping to initiate healing and the repair of tissue. When tissue is damaged, the body responds by sending white blood cells alongside various biochemical substances to the affected area, resulting in increased blood flow and fluid accumulation. This process, although necessary in the short term, can become detrimental when chronic inflammation develops.
Chronic inflammation is linked to numerous health issues, including autoimmune diseases, heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. It occurs when inflammation persists for an extended period, leading to tissue damage and contributing to chronic illness. Understanding how to manage inflammation through lifestyle choices is crucial for optimizing health.
The Role of Anti-inflammatory Foods
One effective method to combat chronic inflammation is through diet. Foods that possess anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce inflammation in the body, thereby decreasing the risk of chronic diseases. Antiinflammatory foods can enhance overall health, promoting longevity and vitality.
Anti-inflammatory foods are typically rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, which can help mitigate oxidative stress and inflammation. This dietary approach encourages the consumption of whole, nutrient-dense foods while minimizing processed items that can trigger inflammatory responses.
Common Causes of Inflammation in the Body
Inflammation can be triggered by a variety of factors. Some common causes include:
- Diet: High sugar intake, excessive consumption of unhealthy fats (trans and saturated fats), and inflammatory foods such as refined grains can lead to increased inflammation.
- Physical Inactivity: Sedentary lifestyles contribute to obesity and promote inflammatory processes.
- Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt hormonal balance and immune function, promoting inflammation.
- Lack of Sleep: Poor sleep patterns have been linked to elevated inflammatory markers in the body.
Top Anti-inflammatory Foods to Incorporate into Your Diet
Berries: Nature’s Antioxidant Powerhouses
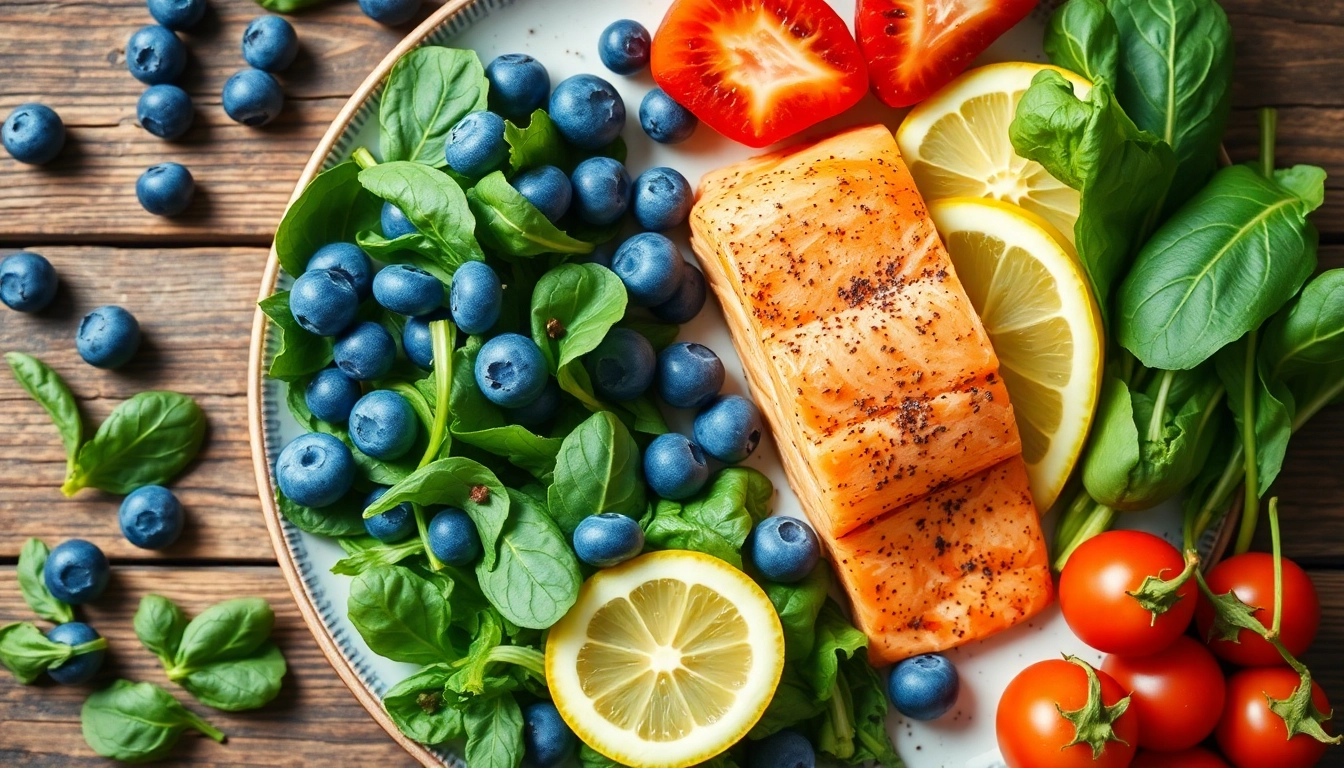
Berries such as blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are incredibly rich in antioxidants, particularly anthocyanins, which confer their vivid colors and anti-inflammatory effects. Research suggests that berries can help reduce markers of inflammation, improve heart health, and provide a range of vitamins and minerals.
Incorporating a variety of berries into your diet can be easy; consider adding them to smoothies, oatmeal, yogurt, or enjoying them as a snack. They not only offer profound health benefits but also satisfy your sweet tooth without added sugars.
Fatty Fish: Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Their Benefits
Fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout, are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3s are known for their potent anti-inflammatory effects, as they inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory compounds. Regular consumption of fatty fish has been linked to lowered risk factors for heart disease, improved brain function, and joint health.
To reap the benefits, aim to include fatty fish in your diet at least twice a week. Preparing grilled or baked fish, or adding it to salads and whole grain dishes, are great options for enjoying these nutrient-packed foods.
Leafy Greens: A Nutrient-dense Addition
Leafy green vegetables, such as spinach, kale, and collard greens, are incredibly nutrient-dense and among the healthiest foods you can eat. They are loaded with antioxidants, vitamins (like A, C, E, and K), and minerals that can combat inflammation and promote health.
These vegetables can be easily included in your meals by adding them to smoothies, salads, stir-fries, or soups. Their versatility and health benefits make them an essential component of an anti-inflammatory diet.
How to Build an Anti-inflammatory Meal Plan
Combining Foods for Maximum Benefit
Creating an anti-inflammatory meal plan involves selecting foods that work synergistically to promote health. Aim to combine different food groups to ensure a wide variety of nutrients. For example:
- Protein: Include lean proteins such as chicken, turkey, tofu, and legumes.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate sources of healthy fats like olive oil, nuts, and avocado to help combat inflammation.
- Whole Grains: Choose whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats which provide fiber and essential nutrients.
This dietary diversity not only supports overall health but also keeps meals interesting and satisfying.
Sample Anti-inflammatory Meal Plans
Here is a sample meal plan that incorporates a variety of anti-inflammatory foods throughout the day:
Breakfast:
Oatmeal topped with berries, chia seeds, and a drizzle of honey.
Lunch:
Spinach salad with grilled salmon, avocado, cherry tomatoes, and a vinaigrette made with olive oil and lemon juice.
Dinner:
Quinoa bowl with roasted vegetables, chickpeas, and a tahini sauce.
Snacks:
Raw almonds, carrot sticks, and hummus.
Shopping Tips for Anti-inflammatory Ingredients
When grocery shopping, consider the following tips to ensure you stock up on anti-inflammatory ingredients:
- Stay Fresh: Choose fresh, organic fruits and vegetables when possible, as they often contain higher nutrient levels.
- Read Labels: Avoid processed foods high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and additives.
- Plan Ahead: Create a list based on your meal plan to avoid impulse buys that might lead to unhealthy choices.
Supplementing Your Diet with Anti-inflammatory Practices
Integrating Exercise for Reduced Inflammation
Physical activity plays a crucial role in managing inflammation. Regular exercise can help reduce inflammation markers while promoting a healthy weight, reducing stress, and improving sleep quality. Aim for a combination of aerobic exercises (like walking, running, or biking) and strength training to maximize benefits.
Stress Management Techniques
Chronic stress has been shown to trigger inflammation in the body. Engaging in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, deep breathing, or even spending time in nature can help mitigate these effects. Prioritize time for relaxation and connect with hobbies that bring joy and peace.
The Importance of Sleep
Sufficient quality sleep is essential for overall health and plays a significant role in regulating inflammation. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep per night. Establish a consistent sleep routine, create a restful sleeping environment, and avoid screens before bedtime to improve sleep quality.
Monitoring Your Progress and Health Improvements
Signs of Reduced Inflammation
As you transition to an anti-inflammatory lifestyle, you may notice several signs of reduced inflammation, including:
- Improved energy levels and vitality
- Reduced joint pain or discomfort
- Better skin health and appearance
- Improved digestion and gut health
How to Adjust Your Diet for Best Results
Monitoring how certain foods affect your body can help you tailor your diet for optimal results. Consider keeping a food diary to track meals and any symptoms you may experience. This practice can highlight food sensitivities and help you refine your anti-inflammatory strategy.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals
For personalized guidance on managing inflammation through diet and lifestyle, consider consulting healthcare professionals such as registered dietitians or nutritionists. They can provide you with tailored advice and support you on your journey towards improved health.